Bandpass Filter
The wavelength band of a certain area is separated from the light source, and the filter that suppresses stray light is called a bandpass filter, which is suitable for large angle incidence to increase the penetration of th transmission area as much as possible. The advantages of the band-pass filter of Ji Aite Optoelectronics are that the spectrum in the band-pass is flat, the isolation of the blocking band is good, the wavelength positioning is accurate, and the IAD coating method is adopted, and the quality is stable and reliable. Application: Criminal detection detection of multi-band light sources, strong light flashlights, fluorescence analysis, iris recognition, surveillance cameras.
Tags: Optical Filter
Hard film bandpass filter structure
Bandpass filters can be constructed by depositing layers of material on the substrate surface. For our hard film bandpass filters, a stack of dielectric films separated by dielectric spacers forms a thin filter stack. Each dielectric stack consists of a large number of material layers with alternating high and low refractive indices. The thickness of each layer in the dielectric film stack is λ/4, where λ is the center wavelength of the bandpass filter (i.e., the wavelength of the maximum transmittance of the filter). The spacer layer is located between the stack of dielectric films and has a thickness of (nλ)/2, where n is an integer. The spacer layer is sandwiched between the two dielectric film stacks to form a Fabry-Perot cavity. To provide protection and ease of operation, the filter is mounted in a metal ring engraved with markings.
Overview of Filter Operation
When the phase-length interference conditions of the Fabry-Perot cavity are met, light in the center wavelength and a small wavelength range on either side of the center wavelength can pass through the filter efficiently, while light outside the passband cannot pass through due to the phase-elimination conditions. However, the bandwidth of the cutoff on both sides of the center wavelength is small. In order to increase the cutoff bandwidth of the filter, a broadband cutoff coating material can be used on the spacer layer or the substrate. Although these materials effectively cut off incident light outside the passband, they also reduce the transmittance in the passband.
Filter Orientation
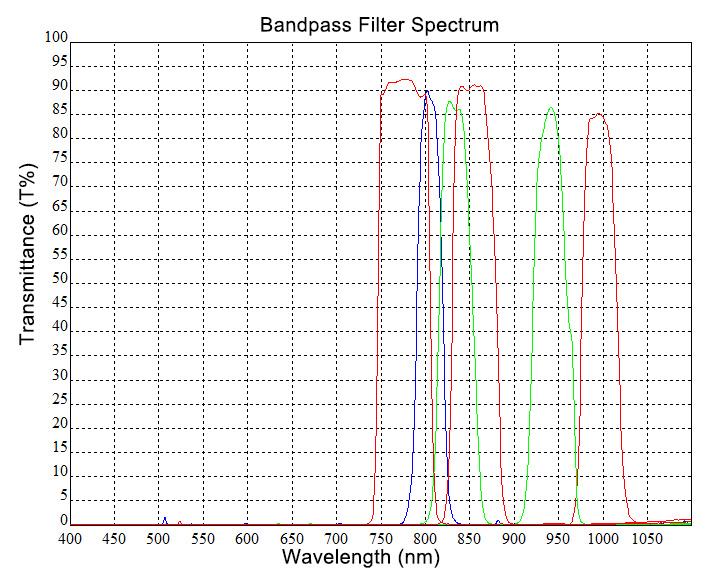
The arrow engraved on the edge of the filter indicates the recommended direction of light transmission through the filter. Orienting the coated side toward the light source reduces unwanted scattering and minimizes reflections back to the light source. However, using the filter in the opposite direction will not significantly affect the performance of the filter. The lower left graph shows the transmittance versus wavelength curve of a filter measured under low-intensity broadband illumination. The figure shows that the direction of incidence has very little effect on the intensity and spectrum of the filter transmission. There is a very small deviation between the forward and reverse transmission curves, which may be due to a very small deviation in the angle of incidence caused when the filter is moved, flipped and replaced.
Filters should be used with collimated light incident squarely on their surfaces. If non-collimated light is used or light is not incident on the filter surface, the center wavelength (the wavelength corresponding to the peak transmittance) will be shifted in the direction of the shorter wavelengths, and the shape of the transmission range (passband) will change. Subtle changes in the angle of incidence tunes the filter passband in a very small range. When the angle of incidence is changed more, the center wavelength is shifted more, and the shape of the passband is significantly distorted, and more importantly, the transmittance of the passband is significantly reduced.
Filter Temperature
The center wavelength of the filter can be slightly adjusted (approximately 1 nm within the filter's operating range) by changing the filter temperature. This is mainly due to slight thermal expansion or contraction of the material layer.
Related Products
Dichroic Mirrors
An optical filter is a device that selectively transmits a portion of the optical spectrum while rej..
Bandpass Filter
Hard film bandpass filter structureBandpass filters can be constructed by depositing layers of mater..
Longpass Filter
A longpass filter, also known as a low-cut filter or a high-pass filter in optics, is a type of opti..
Shortpass Filter
A shortpass filter, also known as a high-cut filter or a low-pass filter in optics, is a type of opt..
Beam Splitter
A beam splitter is an optical device that divides a single incident light beam into two or more sepa..