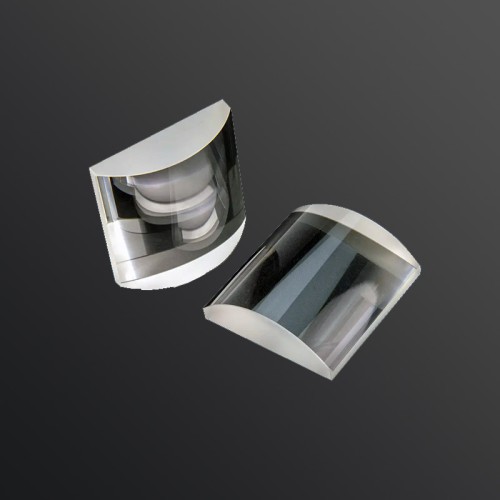
Cylindrical Lens
Cylindrical lenses are optical elements that have curved surfaces in only one dimension, unlike spherical lenses that curve equally in two dimensions. This unique design allows cylindrical lenses to focus or disperse light along one axis only, while leaving the other axis unaffected. Cylindrical lenses are available in both convex and concave forms and are characterized by their ability to refract light in a way that alters the focus along the cylindrical axis without changing the focus perpendicular to it. Their ability to correct optical aberrations and modify light profiles makes them versatile tools in modern optics and optoelectronics.
Tags: Optical Prisms
Cylindrical lenses are optical elements that have curved surfaces in only one dimension, unlike spherical lenses that curve equally in two dimensions. This unique design allows cylindrical lenses to focus or disperse light along one axis only, while leaving the other axis unaffected. Cylindrical lenses are available in both convex and concave forms and are characterized by their ability to refract light in a way that alters the focus along the cylindrical axis without changing the focus perpendicular to it. Their ability to correct optical aberrations and modify light profiles makes them versatile tools in modern optics and optoelectronics.
Key Features of Cylindrical Lenses:
1.One-dimensional Curvature:
The key feature of cylindrical lenses is that they have a curvature along one axis (either horizontally or vertically) and are flat along the other.
2.Anisotropic Focusing:
They focus or diverge light only along their curved axis, maintaining the original direction of light in the perpendicular axis. This is in contrast to spherical lenses, which affect light in both dimensions.
3.Line Focusing:
Convex cylindrical lenses can be used to focus a line of light or an image in one dimension, which is useful in applications requiring linear focusing.
4.Image Correction:
They are used to correct astigmatism in optical systems or vision, compensating for differences in the refractive power of the eye along different axes.
5.Anamorphic Optics:
In combination with spherical lenses, cylindrical lenses can be used to change the aspect ratio of an image or reshape light beams, which is crucial in some projection and imaging systems.
Applications of Cylindrical Lenses:
1.Bar Code Scanning:
In barcode readers, cylindrical lenses are used to focus the laser line accurately onto the barcode, ensuring reliable scanning.
2.Line Illumination:
They are employed to create uniform illumination along a line, useful in machine vision systems for inspection and measurement tasks.
3.Anamorphic Beam Shaping:
In laser systems, cylindrical lenses can transform circular laser beams into elliptical or linear profiles, which is useful for laser cutting, engraving, or alignment applications.
4.Optical Correction:
In eyeglasses and contact lenses, cylindrical components correct for astigmatism by compensating for irregularities in the cornea's curvature.
5.Telecentric Lenses:
In telecentric optical systems, cylindrical lenses are sometimes incorporated to maintain orthographic projection, which is important in high-precision measurement and machine vision applications.
Factors Affecting Function:
- Axis of Curvature:
The orientation of the curved axis relative to the optical system's requirements is critical for proper function.
- Curvature Radius:
The radius of curvature along the cylindrical axis determines the degree of focusing or diverging effect.
- Length and Diameter:
The length of the cylinder affects the size of the focused line or the extent of the beam shaping, while the diameter impacts the light-gathering capacity.

