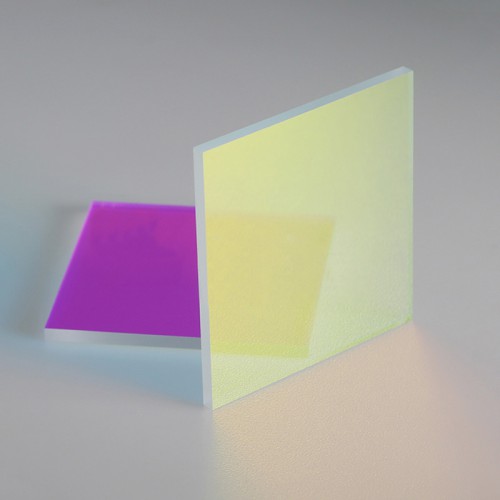
Beam Splitter
A beam splitter is an optical device that divides a single incident light beam into two or more separate beams. It plays a crucial role in various optical setups and applications where splitting, combining, or redirecting light beams is necessary. Beam splitters can be designed to divide light evenly or unequally between the output paths, depending on the application requirements.
Tags: Optical Filter
A beam splitter is an optical device that divides a single incident light beam into two or more separate beams. It plays a crucial role in various optical setups and applications where splitting, combining, or redirecting light beams is necessary. Beam splitters can be designed to divide light evenly or unequally between the output paths, depending on the application requirements.
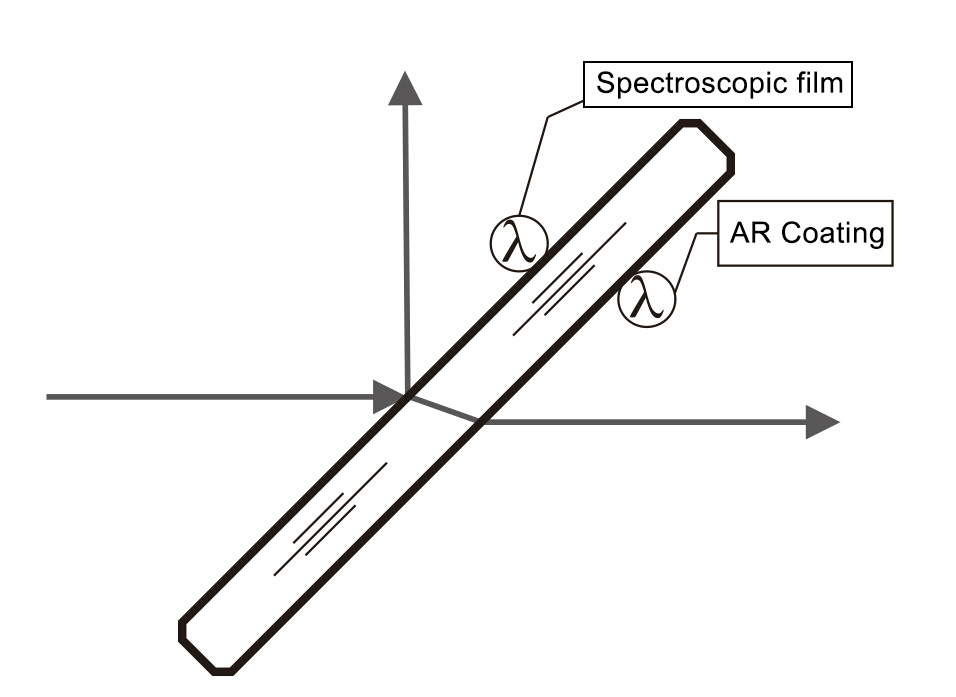
Types of Beam Splitters:
1.Plate Beam Splitters:
These are the most common type, consisting of a flat piece of glass or other transparent material with a partially reflective coating on one surface. The coating is designed to reflect a certain percentage of the incoming light and transmit the rest. The reflection and transmission ratios can be tailored by adjusting the properties of the coating.
2.Cube Beam Splitters:
Instead of a flat plate, cube beam splitters use two triangular prisms bonded together at their hypotenuses with a partially reflective coating at the interface. This design offers improved stability, minimal beam deviation, and can handle a wider range of incident angles without affecting performance.
3.Polarizing Beam Splitters:
Specialized coatings or crystal materials are used to split light based on polarization. They transmit light of one polarization state and reflect light of the orthogonal polarization state, enabling advanced control in polarization-sensitive applications.
4.Fiber Optic Beam Splitters:
Used in fiber optic systems, these devices split the light within a single optical fiber into two or more fibers. They are often fabricated by tapering or etching the fiber to induce the splitting effect.
Operating Principles:
Beam splitters operate based on the principles of reflection and transmission. The efficiency of a beam splitter is determined by the quality of its coating or material, which is designed to reflect and transmit specific fractions of the incident light. The coating is usually made from dielectric materials that create interference effects to achieve the desired reflection and transmission characteristics.
Applications:
Beam splitters find extensive use in a variety of fields, including:
1.Interferometry:
Essential in interferometric setups where the division of a light source into reference and measurement beams is required for highly accurate distance or surface measurements.
2.Optical Networking and Telecommunications:
Used to split or combine optical signals in fiber optic communication systems.
3.Laser Systems:
In complex laser setups, beam splitters are used to direct laser beams to multiple locations or to combine beams for increased power or interference effects.
4.Imaging and Photography:
Enables techniques like split-view photography or as a component in viewfinders, where part of the image is directed to a camera sensor and another part to a separate viewer.
5.Medical Imaging:
Crucial in optical coherence tomography (OCT) and other medical diagnostic equipment that relies on dividing light for imaging internal structures.
6.Entertainment Industry:
Used in special effects, projection systems, and stage lighting to create visual effects or manage light distribution.
Related Products
Dichroic Mirrors
An optical filter is a device that selectively transmits a portion of the optical spectrum while rej..
Bandpass Filter
Hard film bandpass filter structureBandpass filters can be constructed by depositing layers of mater..
Shortpass Filter
A shortpass filter, also known as a high-cut filter or a low-pass filter in optics, is a type of opt..