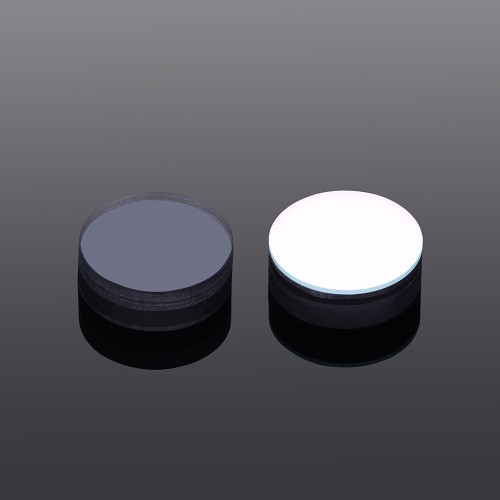
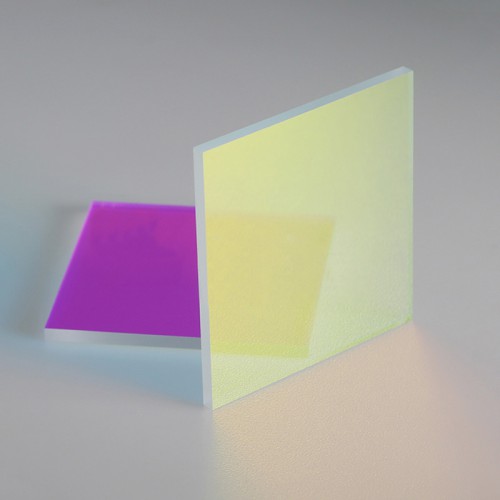
Dichroic Mirrors
Dichroic mirrors, also called dichroic mirrors, are often used in laser technology. Its characteristic is that the light of a certain wavelength is almost completely transmitted, while the light of other wavelengths is almost completely reflected.
Tags: Optical Filter
An optical filter is a device that selectively transmits a portion of the optical spectrum while rejecting the transmission of other wavelengths. Depending on the means by which filters block unwanted wavelengths, they can be classified as either dichroic or absorptive.Dichroic mirror is an optical component that selectively reflects certain wavelengths (colors) of light while transmitting others. This is achieved through the interference properties of thin-film coatings deposited on the surface of the mirror. These coatings are designed to have different refractive indices and thicknesses, which enables them to reflect specific wavelengths based on the principles of optical interference. It is often used in sensor systems such as fluorescence microscope systems of enzyme label instruments, projection light engine systems, laser lights, optical instrument beam splitters, and video eyes. It is an optical component that optical designers are enthusiastically pursuing. The structure of the device can be effectively reduced to realize a multifunctional optical path.
Types of Dichroic Mirrors
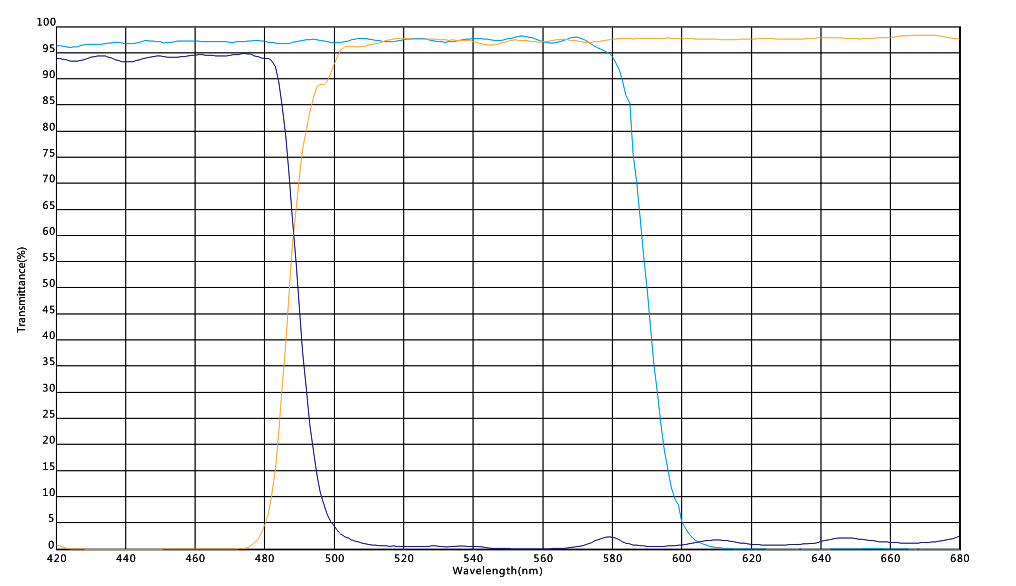
Dichroic mirrors are classified by the way in which they transmit light. Types of dichroic mirrors include longpass dichroic mirrors, shortpass dichroic mirrors, and multi band dichroic mirrors. Hot and cold mirrors used to reflect or otherwise suppress unwanted heat in thermal sensitive applications are also dichroic mirrors.
Longpass dichroic mirrors will have a cut-on wavelength that separates a highly reflective and transmissive band. Longer wavelengths, above the cut on wavelength, are freely transmitted through the mirror, while shorter wavelengths are reflected back.
A shortpass dichroic mirror features a cut-off wavelength. Radiation above the cut-off wavelength experiences high reflectance, while radiation below the cut-off wavelength is transmitted.
Multi-band dichroic mirrors have both a cut-off and cut-on wavelength, and two transmission bands as well as one reflective band. The wavelength range between the cut-off and cut-on wavelength is highly reflective, while wavelength ranges above the cut-on and below the cut-off wavelengths are highly transmissive.
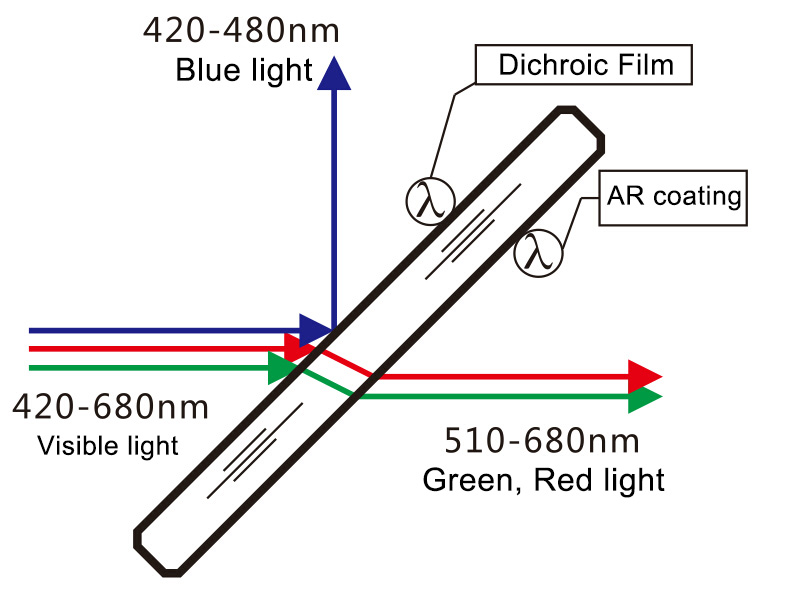
Dichroic mirrors find extensive use in many optical systems and instruments, including:
Optical Imaging
In fluorescence microscopy, they are used to separate the excitation light from the emitted fluorescence, allowing clear visualization of specific stained samples.
Laser Systems
They can be used to combine or separate laser beams of different wavelengths in laser-based applications such as laser shows, medical equipment, or industrial material processing.
Entertainment
LightingIn stage lighting and special effects, dichroic filters are used to create color effects by reflecting certain colors while transmitting others.
Telecommunications
They play a role in wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) systems, where multiple signals of different wavelengths are combined or separated for transmission along optical fibers.
Related Products
Dichroic Mirrors
An optical filter is a device that selectively transmits a portion of the optical spectrum while rej..
Narrow Bandpass Filter
A narrow band optical filter is a type of optical filter that allows the transmission of a very spec..
Bandpass Filter
Hard film bandpass filter structureBandpass filters can be constructed by depositing layers of mater..
Longpass Filter
A longpass filter, also known as a low-cut filter or a high-pass filter in optics, is a type of opti..
Shortpass Filter
A shortpass filter, also known as a high-cut filter or a low-pass filter in optics, is a type of opt..
Beam Splitter
A beam splitter is an optical device that divides a single incident light beam into two or more sepa..