Shortpass Filter
A shortpass filter, also known as a high-cut filter or a low-pass filter in optics, is a type of optical filter designed to transmit wavelengths shorter than a specified cutoff wavelength and to block or significantly attenuate wavelengths longer than this cutoff point. It essentially functions as the opposite of a longpass filter, setting a maximum threshold for the wavelengths allowed to pass through.
Tags: Optical Filter
A shortpass filter, also known as a high-cut filter or a low-pass filter in optics, is a type of optical filter designed to transmit wavelengths shorter than a specified cutoff wavelength and to block or significantly attenuate wavelengths longer than this cutoff point. It essentially functions as the opposite of a longpass filter, setting a maximum threshold for the wavelengths allowed to pass through.
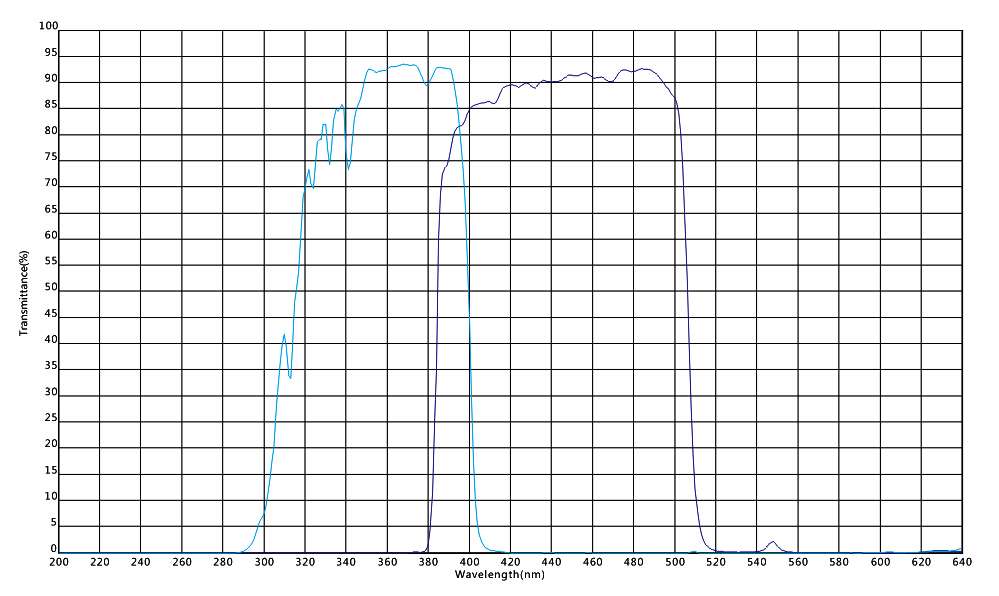
Key Features of Shortpass Filters:
1.Cutoff Wavelength (λc):
This is the wavelength at which the filter starts to significantly attenuate or block light. Above this wavelength, transmission decreases rapidly.
2.Transition Width:
Similar to longpass filters, this describes the range over which the filter transitions from high transmission to low transmission or blocking. A narrow transition width is preferred for applications that require a sharp distinction between passed and blocked wavelengths.
3.Passband Transmission:
Refers to how efficiently the filter transmits wavelengths below the cutoff point. High transmission in the passband is desirable for most applications.
4.Blocking Range Transmission:
Measures how effectively the filter blocks wavelengths above the cutoff. An ideal shortpass filter should have very low transmission in this range to prevent contamination from unwanted longer wavelengths.
Applications of Shortpass Filters:
Shortpass filters are integral components in various optical systems where filtering out longer wavelengths is necessary:
1.Fluorescence Microscopy and Spectroscopy:
They are used to isolate the emission wavelengths of fluorescent markers from the excitation light, which is typically of a longer wavelength.
2.UV Photography and Sensing:
In applications where only ultraviolet light needs to be captured or detected, a shortpass filter that cuts off in the visible or infrared range is employed.
3.Daylight Harvesting and Solar Energy:
To maximize the efficiency of solar panels or daylighting systems, shortpass filters can be used to remove infrared heat from sunlight, thereby reducing thermal load and optimizing the energy input.
4.Laser Systems:
They help purify laser beams by removing unwanted longer-wavelength components, ensuring the laser operates at the intended short wavelengths.
5.Display Technology:
In LCD and OLED displays, shortpass filters are used to remove unwanted wavelengths from backlight sources, improving color purity and contrast.
Types of Shortpass Filters:
- Interference Shortpass Filters:
These filters use multiple layers of thin films to create an interference effect that reflects longer wavelengths while transmitting shorter ones. They can achieve very sharp cutoffs and high transmission in the passband.
- Absorptive Shortpass Filters:
Made from materials that absorb wavelengths above the cutoff point, these filters gradually decrease transmission as the wavelength increases. They are simpler in construction but may not offer as sharp a cutoff as interference filters.
Selecting the appropriate type of shortpass filter depends on the specific application requirements, such as the desired cutoff wavelength, the required steepness of the transition, and the level of blocking needed in the rejection band.
Related Products
Dichroic Mirrors
An optical filter is a device that selectively transmits a portion of the optical spectrum while rej..
Bandpass Filter
Hard film bandpass filter structureBandpass filters can be constructed by depositing layers of mater..
Longpass Filter
A longpass filter, also known as a low-cut filter or a high-pass filter in optics, is a type of opti..
Beam Splitter
A beam splitter is an optical device that divides a single incident light beam into two or more sepa..